Body Fluids
 Back to Urinalysis
Back to Urinalysis
Jump to: Synovial Fluid | CSF | Semen | Amniotic Fluid | Serous Fluid
*If you find this section helpful and you know who Brenda is, say "thank you" to her and give her chocolate.
Synovial Fluid
Purpose: lubricant—absorb shock
Classifications
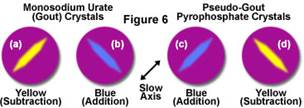
Synovial Crystals
| Uric acid (monosodium urate) | Gout |
Calcium pyrophosphate |
Pseudogout |
Cholesterol |
Chronic arthritis conditions (RA) |
Apatite |
Mineral in cartilage – arthritis |
Corticosteroid |
From drug injection |
CSF
Purpose: supply nutrients, remove waste, and cushion
Produced in choroid plexus, flows between arachnoid and pia mater
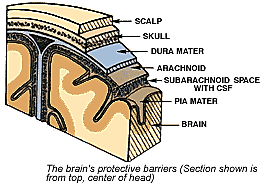
Indications
Hemorrhage, neurologic infections, malignancy, tumors
Counterindications
Septicemia, systemic infection, localized lumbar infection
Normal Reference Ranges
|
Adult |
Neonates |
WBC |
<5 |
<30 |
RBC |
0 |
0 |
Lymphs |
40-80% |
5-35% |
Macrophages |
15-45% |
50-90% |
Neutrophils |
0-6% |
0-8% |
Protein |
15-45 mg/dL |
15-45 mg/dL |
Glucose |
50-80 mg/dL* |
50-80 mg/dL* |
*Glucose is 60-70% plasma concentration

CSF—Abnormal Findings
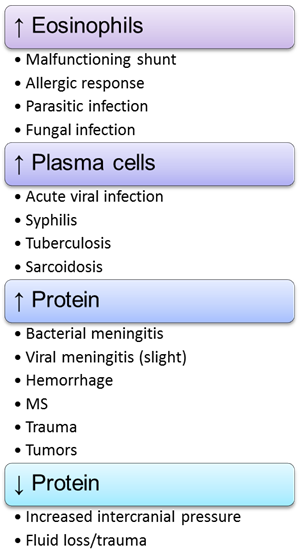
Abnormal Proteins
Oligoclonal bands in gamma region = MS
Myelin basic protein (from nerve sheath) : used to monitor MS
Normal Proteins
Albumin – most, Prealbumin, Tau Transferrin (unique to CSF), IgG – small amount
Electrolytes in CSF
Ca, Cl, Mg, K, Na, Lactate
Lactate is used to differentiate bacterial ↑ vs. viral ↓ meningitis
Glucose
↓ bacterial meningitis,↓ tubercular meningitis, Normal in viral meningitis
Microbiology

Semen
Reference RangesVolume : >1.9 ml 2-5ml
Viscosity : drops
Count : >39 million 20-160
Motility : 50-100%
Index : >2
Morphology : <30% abnormal
Other Infertility Tests
- Sperm viability: eosin-nigrosin stain
- Dead stain red (unable to keep eosin out)
- Fructose: ↓ means lack of support medium produced by seminal vesicles
- Sperm agglutinins: Ab in male or female plasma causes agglutination of sperm
- Varicocele: hardening of veins draining testes – most common cause of infertility
Amniotic Fluid
Formed from- Metabolism of fetal cells
- Transfer of H2O across placental membrane
- In 3rd trimester, fetal urine
- Baby begins to swallow fluid at this point, so input & output are equal, therefor fluid does not build up
Bilirubin: test to check for RBC destruction due to maternal Rh Ab
Lecithin-sphingomyelin ratio
- Lecithin: from alveolar lining, produced at a constant rate until 35th week
- Sphingomyelin: produced at a constant rate after 26th week
- L/S ratio ≥ 2.0 : preterm delivery safe
The Shake Test (foam test)
95% ethanol + amniotic fluid --> shake --> sit 15 min.
A thin line of bubbles lining outside edge = lung maturity
Creatinine: at 36 weeks urine appears in amniotic fluid, ~ concentration of >2 mg/dl
Phosphatidylglycerol: lipid not found in blood and it parallels lecithin (except in diabetic moms)
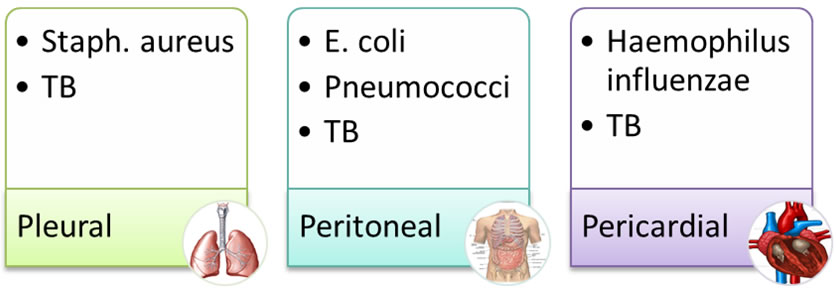
Serous Fluid
Pleural (thorasic), Pericardial, and Peritoneal (ascites)
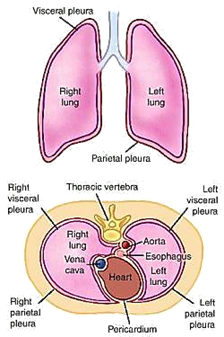
Purpose: Lubrication of parietal and visceral membranes
- Parietal membrane lines cavity wall
- Visceral membrane covers organs
Production: an ultrafiltrate of plasma, maintained by pressure (osmotic and hydrostatic forces) and is reabsorbed into the lymphatic system

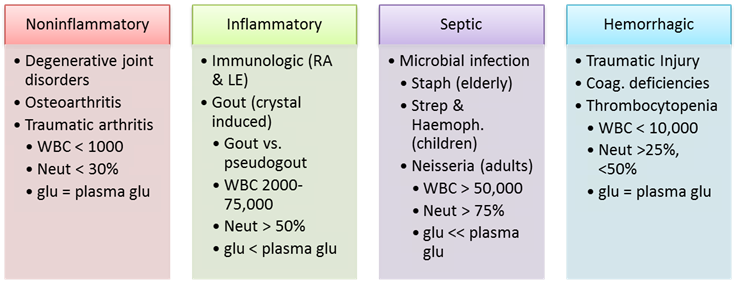
Exudate vs. Transudate
|
Exudate |
Transudate |
Appearance |
|
Clear – pale yellow (normal) |
Source |
↑ Capillary permeability |
↑Hydrostatic (blood) pressure |
Due to |
Conditions involving membranes of cavity |
Systemic disorders |
|
Inflammatory Process
|
Noninflammatory Process
|
|
Requires further testing |
No further testing needed |
|
> 1000 WBC (pleural) |
< 1000 WBC (pleural) |
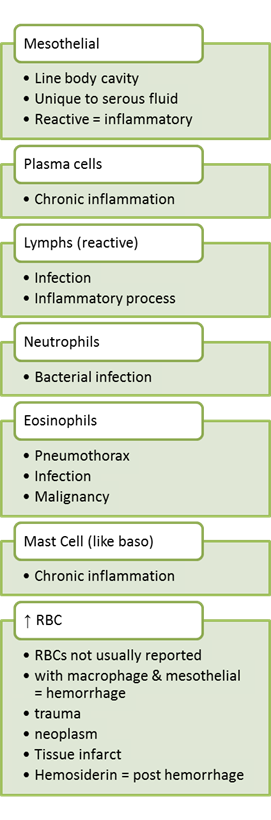
Serous fluid – cell types and significance
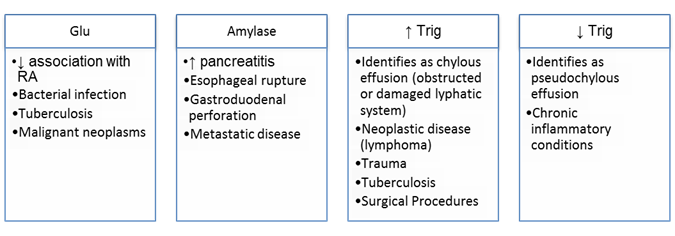
Enzymes & Significance
TP & LDH classify fluid as exudate or transudate
Then:
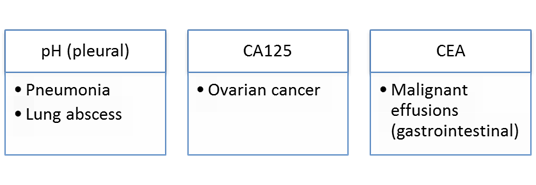
Common Organisms in Serous Fluid